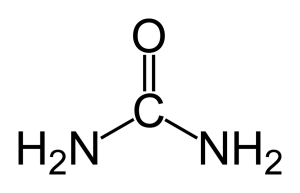
 Urea CO(NH2)2 is a non toxic nitrogen source that’s highly soluble in water. It is probably the cheapest commercial source of nitrogen available today and has the highest nitrogen content of all commonly used solid nitrogenous fertilizers.
Urea CO(NH2)2 is a non toxic nitrogen source that’s highly soluble in water. It is probably the cheapest commercial source of nitrogen available today and has the highest nitrogen content of all commonly used solid nitrogenous fertilizers.
Urea is an excellent nutrient for spirulina, but its concentration in the medium must be kept low (below 60 mg/liter). Urea is made up of ammonia and CO2, known also as Carbamide, with an NPK ratio of 46-0-0 and is found in urine and agricultural & urban waste.
A faint smell of ammonia from the grow environment normally indicates an excess of nitrogen, not necessarily harmful. However, a strong odor is an indication of an overdose which is a threat to spirulina culture and needs to be addressed immediately.
Urea is used in many spirulina growth mediums as well as in routine feeding in order to maintain a healthy, thriving culture. A natural alternative to urea can be human urine, which is ideal for feeding Spirulina, with an NPK ratio of 11-1-2.5.
« Back to Glossary Index